7 min read
Preparations for Next Moonwalk Simulations Underway (and Underwater)
2024 intro: As NASA’s Ames Research Center in California’s Silicon Valley enters its 85th year since its founding, join us as we take a look back at some of our highlights of science, engineering, research, and innovation from 2024.
Ames Arc Jets Play Key Role in Artemis I Orion Spacecraft Heat Shield Findings
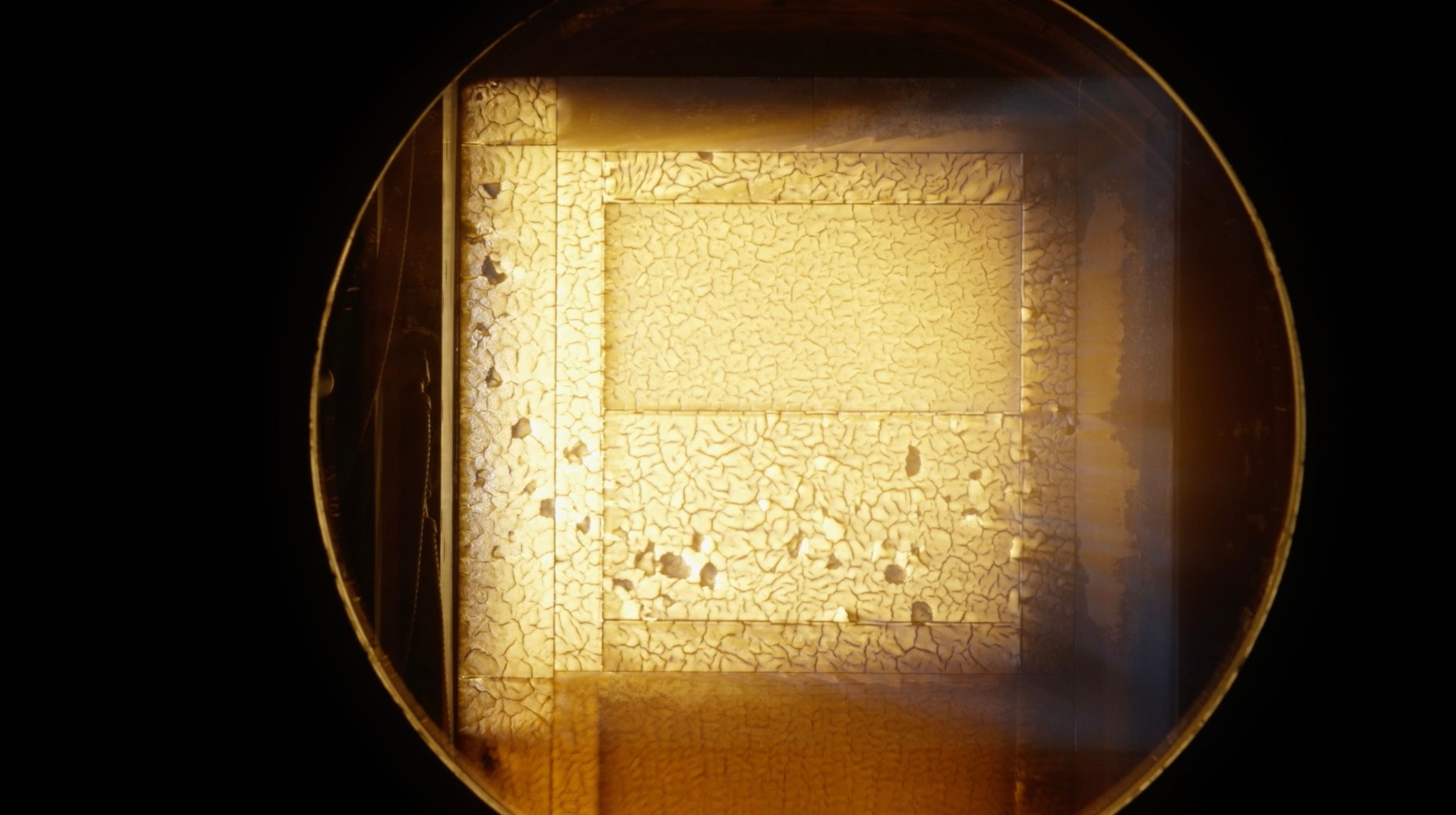
Researchers at Ames were part of the team tasked to better understand and identify the root cause of the unexpected char loss across the Artemis I Orion spacecraft’s heat shield. Using Avcoat material response data from Artemis I, the investigation team was able to replicate the Artemis I entry trajectory environment — a key part of understanding the cause of the issue — inside the arc jet facilities at NASA Ames.
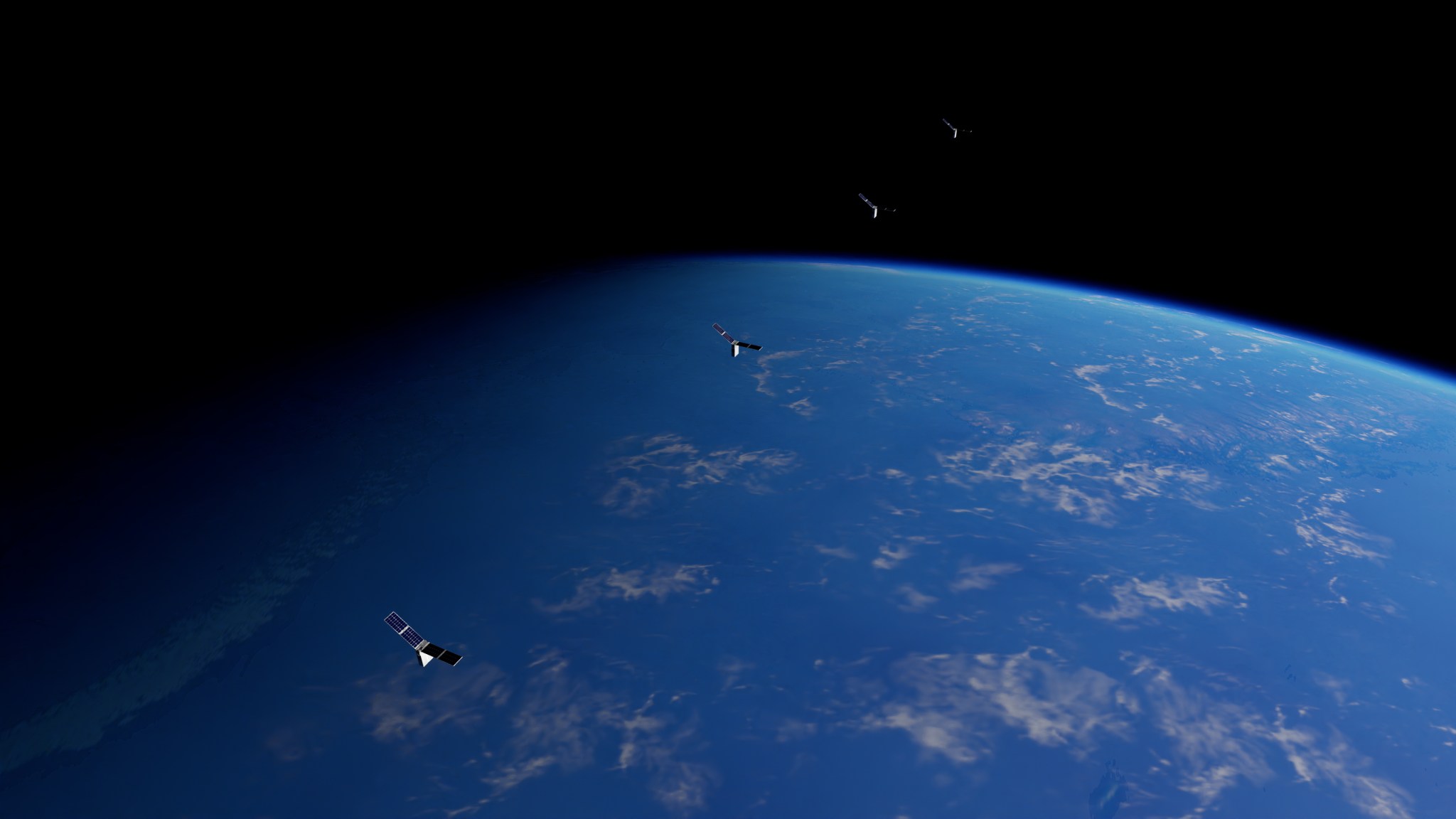
Starling Swarm Completes Primary Mission
After ten months in orbit, the Starling spacecraft swarm successfully demonstrated its primary mission’s key objectives, representing significant achievements in the capability of swarm configurations in low Earth orbit, including distributing and sharing important information and autonomous decision making.
Another Step Forward for BioNutrients
NASA’s BioNutrients entered its fifth year in its mission to investigate how microorganisms can produce on-demand nutrients for astronauts during long-duration space missions. Keeping astronauts healthy is critical and as the project comes to a close, researchers have processed production packs on Earth on the same day astronauts processed production packs in space on the International Space Station to demonstrate that NASA can produce nutrients after at least five years in space, providing confidence it will be capable of supporting crewed missions to Mars.
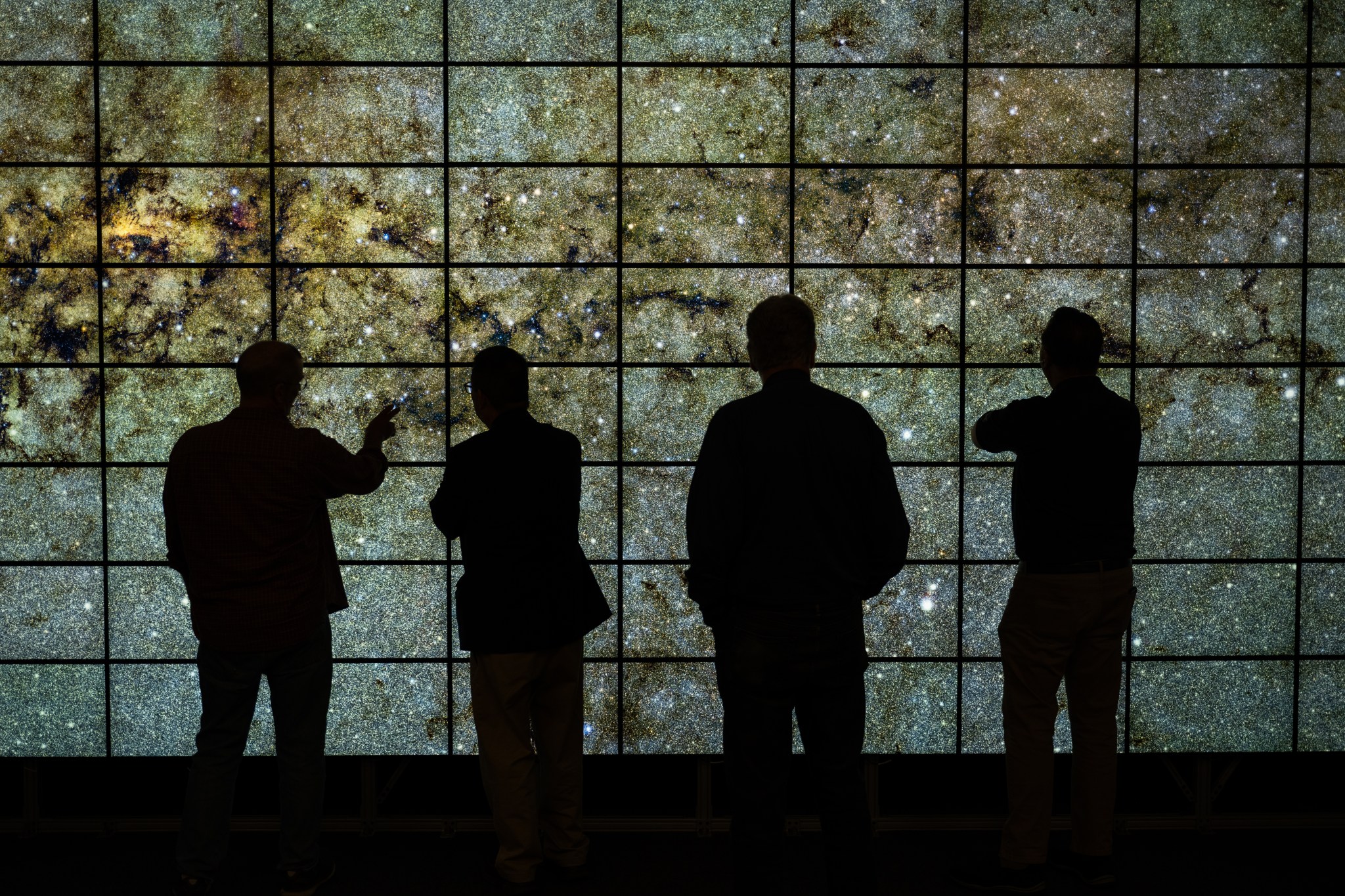
Hyperwall Upgrade Helps Scientists Interpret Big Data
Ames upgraded its powerful hyperwall system, a 300-square foot wall of LCD screens with over a billion pixels to display supercomputer-scale visualizations of the very large datasets produced by NASA supercomputers and instruments. The hyperwall is just one way researchers can utilize NASA’s high-end computing technology to better understand their data and advance the agency’s missions and research.
Ames Contributions to NASA Artificial Intelligence Efforts

Ames contributes to the agency’s artificial intelligence work through ongoing research and development, agencywide collaboration, and communications efforts. This year, NASA announced David Salvagnini as its inaugural chief artificial intelligence officer and held the first agencywide town hall on artificial intelligence sharing how the agency is safely using and developing artificial intelligence to advance missions and research.
Advanced Composite Solar Sail System Successfully Launches, Deploys Sail
NASA’s Advanced Composite Solar Sail System successfully launched from Māhia, New Zealand, in April, and successfully deployed its sail in August to begin mission operations. The small satellite represents a new future in solar sailing, using lightweight composite booms to support a reflective polymer sail that uses the pressure of sunlight as propulsion.
Understanding Our Planet
In 2024, Ames researchers studied Earth’s oceans and waterways from multiple angles – from supporting NASA’s Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem, or PACE, mission to bringing students in Puerto Rico experiences in oceanography and the preservation of coral reefs. Working with multiple partners, our scientists and engineers helped inform ecosystem management by joining satellite measurements of Earth with animal tracking data. In collaboration with the U.S. Geological Survey, a NASA team continued testing a specialized instrument package to stay in-the-know about changes in river flow rates.
Revealing the Mysteries of Asteroids in Our Solar System
Ames researchers used a series of supercomputer simulations to reveal a potential new explanation for how the moons of Mars may have formed: The first step, the findings say, may have involved the destruction of an asteroid.
Using NASA’s powerful James Webb Space Telescope, another Ames scientist helped reveal the smallest asteroids ever found in the main asteroid belt.
Ames Helps Emerging Space Companies ‘Take the Heat’
A heat shield material invented and made at Ames helped to safely return a spacecraft containing the first product processed on an autonomous, free-flying, in-space manufacturing platform. February’s re-entry of the spacecraft from Varda Space Industries of El Segundo, California, in partnership with Rocket Lab USA of Long Beach, California, marked the first time a NASA-manufactured thermal protection material, called C-PICA (Conformal Phenolic Impregnated Carbon Ablator), ever returned from space.
Team Continues to Move Forward with Mission to Learn More about Our Star
HelioSwarm’s swarm of nine spacecraft will provide deeper insights into our universe and offer critical information to help protect astronauts, satellites, and communications signals such as GPS. The mission team continues to work toward launching in 2029.
CAPSTONE Continues to Chart a New Path Around the Moon
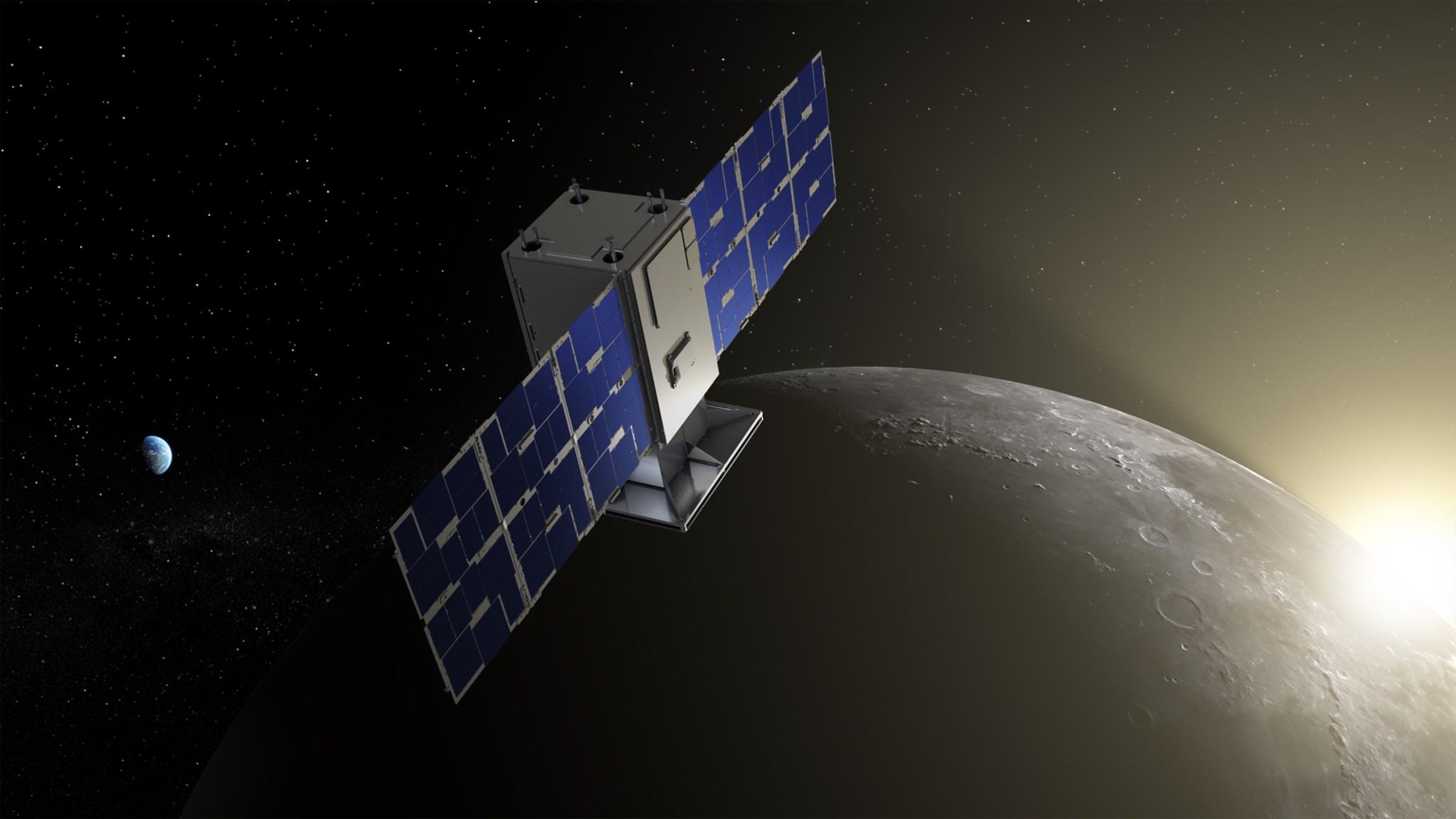

The microwave sized CubeSat, CAPSTONE, continues to fly in a cis-lunar near rectilinear halo orbit after launching in 2022. Flying in this unique orbit continues to pave the way for future spacecraft and Gateway, a Moon-orbiting outpost that is part of NASA’s Artemis campaign, as the team continues to collect data.
NASA Moves Drone Package Delivery Industry Closer to Reality
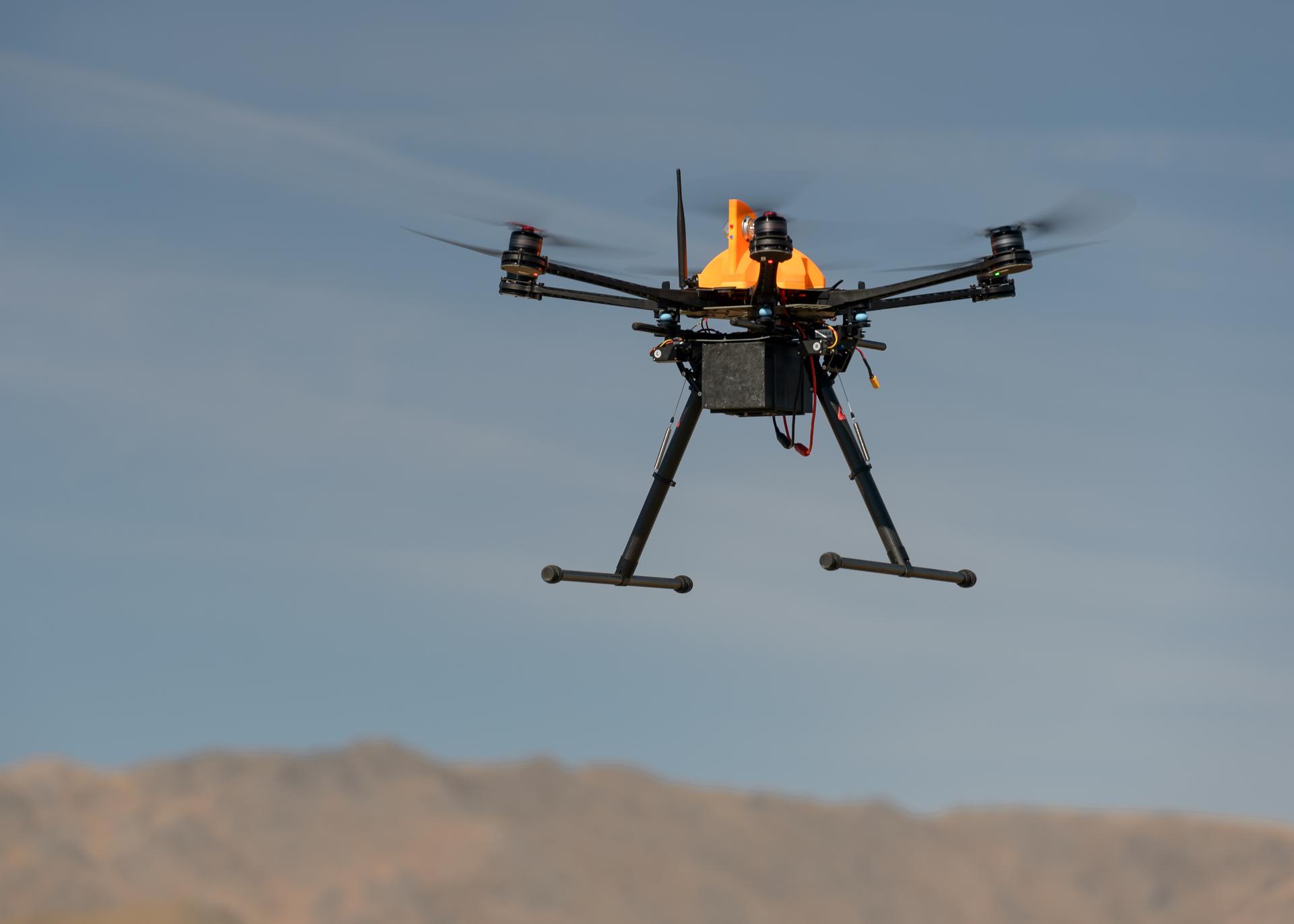

NASA’s uncrewed aircraft system traffic management concepts paved the way for newly-approved package delivery drone flights in the Dallas area.
NASA Technologies Streamline Air Traffic Management Systems
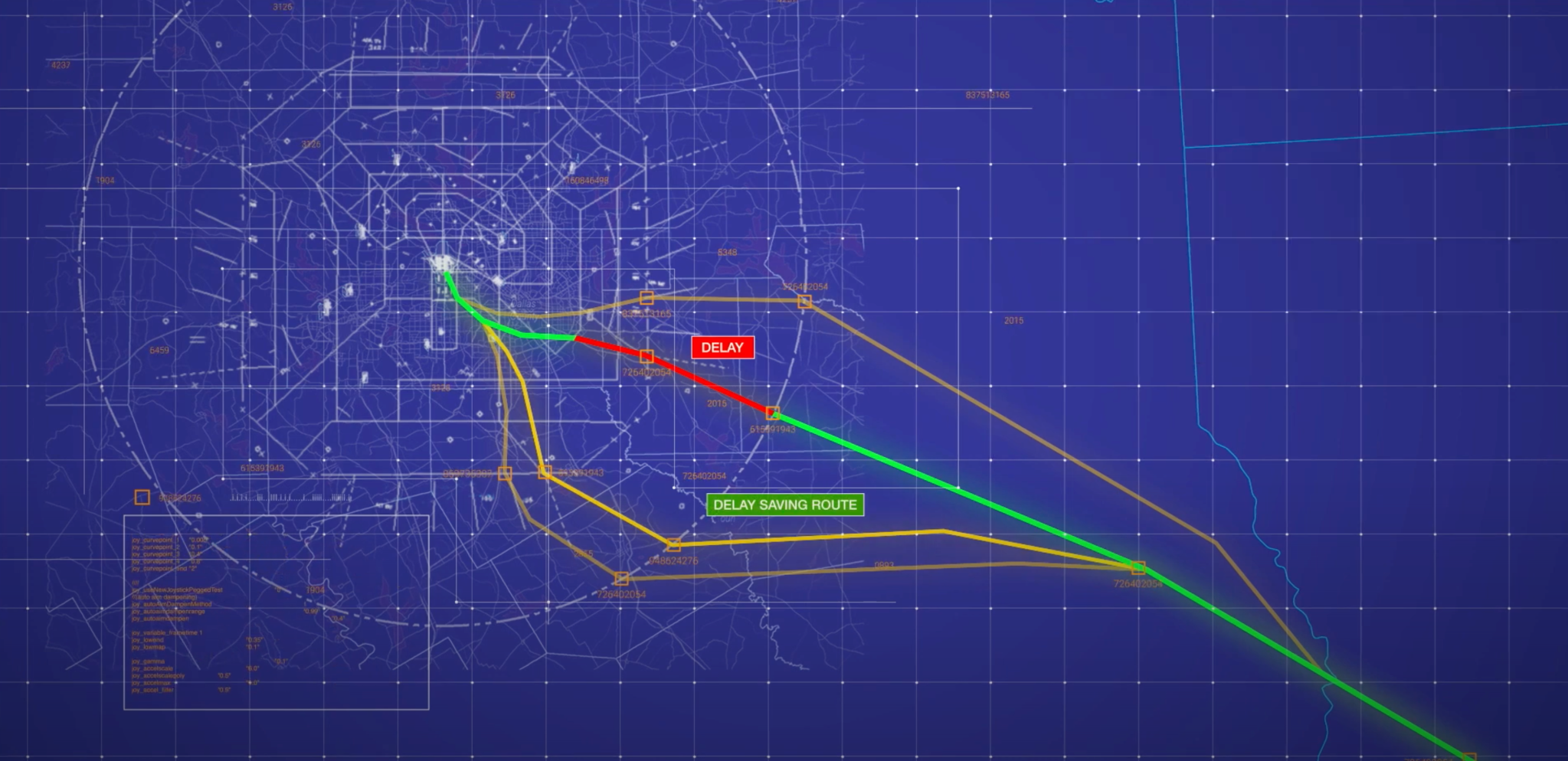
Managing our busy airspace is a complex and important issue, ensuring reliable and efficient movement of commercial and public air traffic as well as autonomous vehicles. NASA, in partnership with AeroVironment and Aerostar, demonstrated a first-of-its-kind air traffic management concept that could pave the way for aircraft to safely operate at higher altitudes. The agency also saw continued fuel savings and reduction in commercial flight delays at Dallas Fort-Worth Airport, thanks to a NASA-developed tool that allows flight coordinators to identify more efficient, alternative takeoff routes.
Small Spacecraft Gathers Big Solar Storm Data from Deep Space
BioSentinel – a small satellite about the size of a cereal box – is currently more than 30 million miles from Earth, orbiting our Sun. After launching aboard NASA’s Artemis I more than two years ago, BioSentinel continues to collect valuable information for scientists trying to understand how solar radiation storms move through space and where their effects – and potential impacts on life beyond Earth – are most intense. In May 2024, the satellite was exposed to a coronal mass ejection without the protection of our planet’s magnetic field and gathered measurements of hazardous solar particles in deep space during a solar storm.
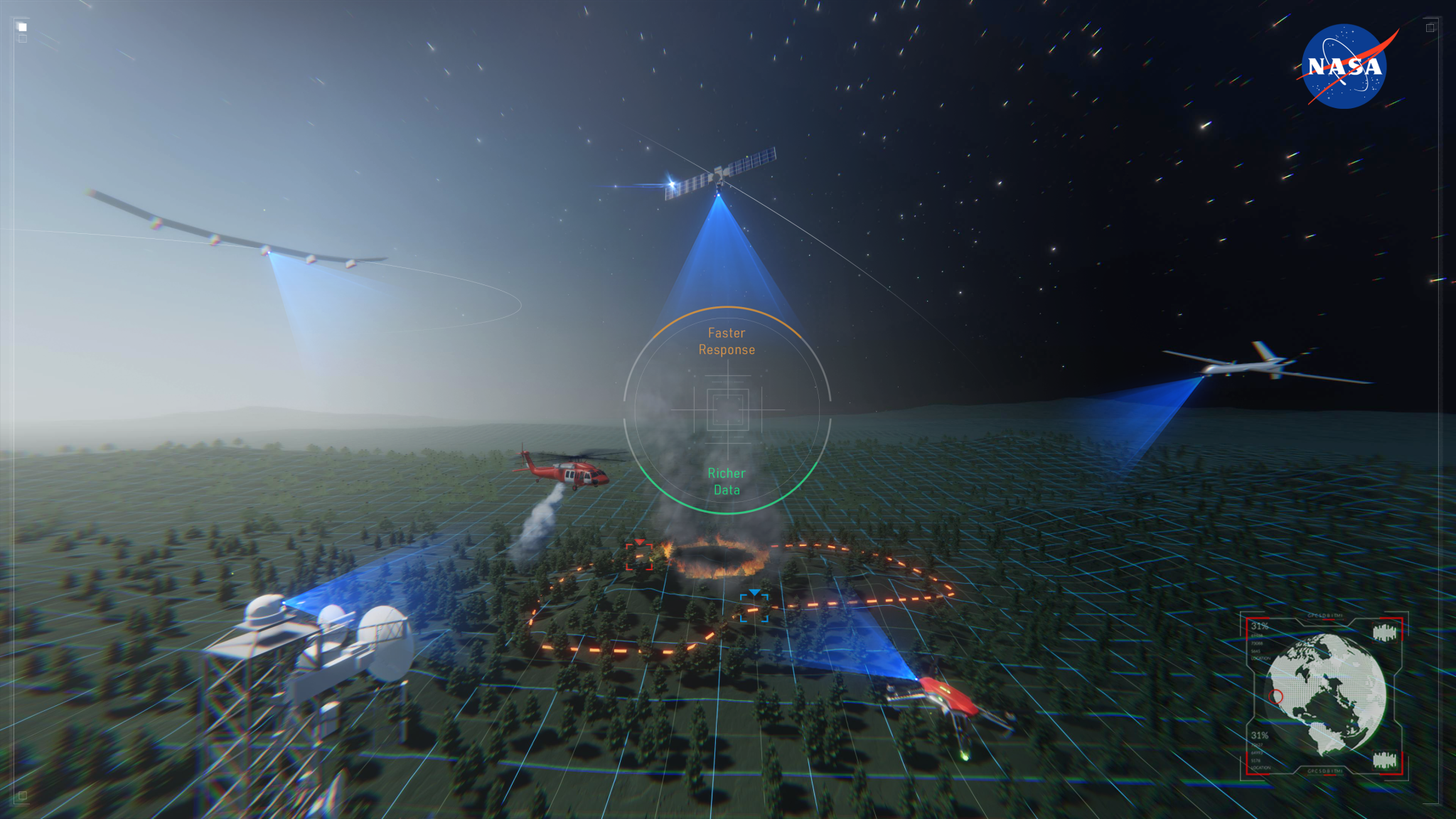
NASA, FAA Partner to Develop New Wildland Fire Technologies
NASA researchers continued to develop and test airspace management technologies to enable remotely-piloted aircraft to fight and monitor wildland fires 24 hours a day.
The Advanced Capabilities for Emergency Response Operations (ACERO) project seeks to use drones and advanced aviation technologies to improve wildland fire coordination and operations.
NASA and Forest Service Use Balloon to Help Firefighters Communicate
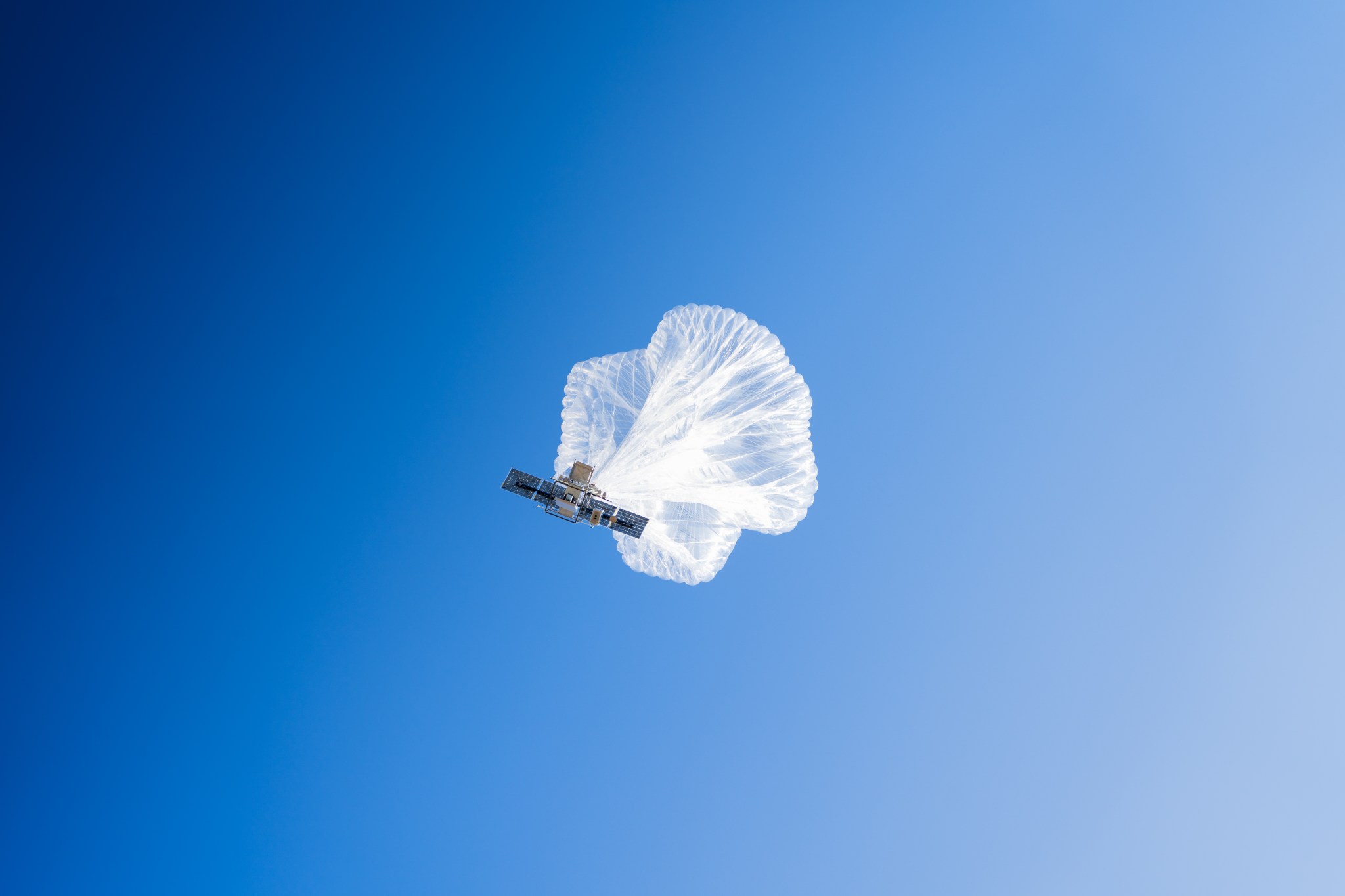

The Strategic Tactical Radio and Tactical Overwatch (STRATO) technology is a collaborative effort to use high-altitude balloons to improve real-time communications among firefighters battling wildland fires. Providing cellular communication from above can improve firefighter safety and firefighting efficiency.
A Fully Reimagined Visitor Center
The NASA Ames Visitor Center at Chabot Space & Science Center in Oakland, California includes a fully reimagined 360-degree experience, featuring new exhibits, models, and more. An interactive exhibit puts visitors in the shoes of a NASA Ames scientist, designing and testing rovers, planes, and robots for space exploration.
Ames Collaborations in the Community
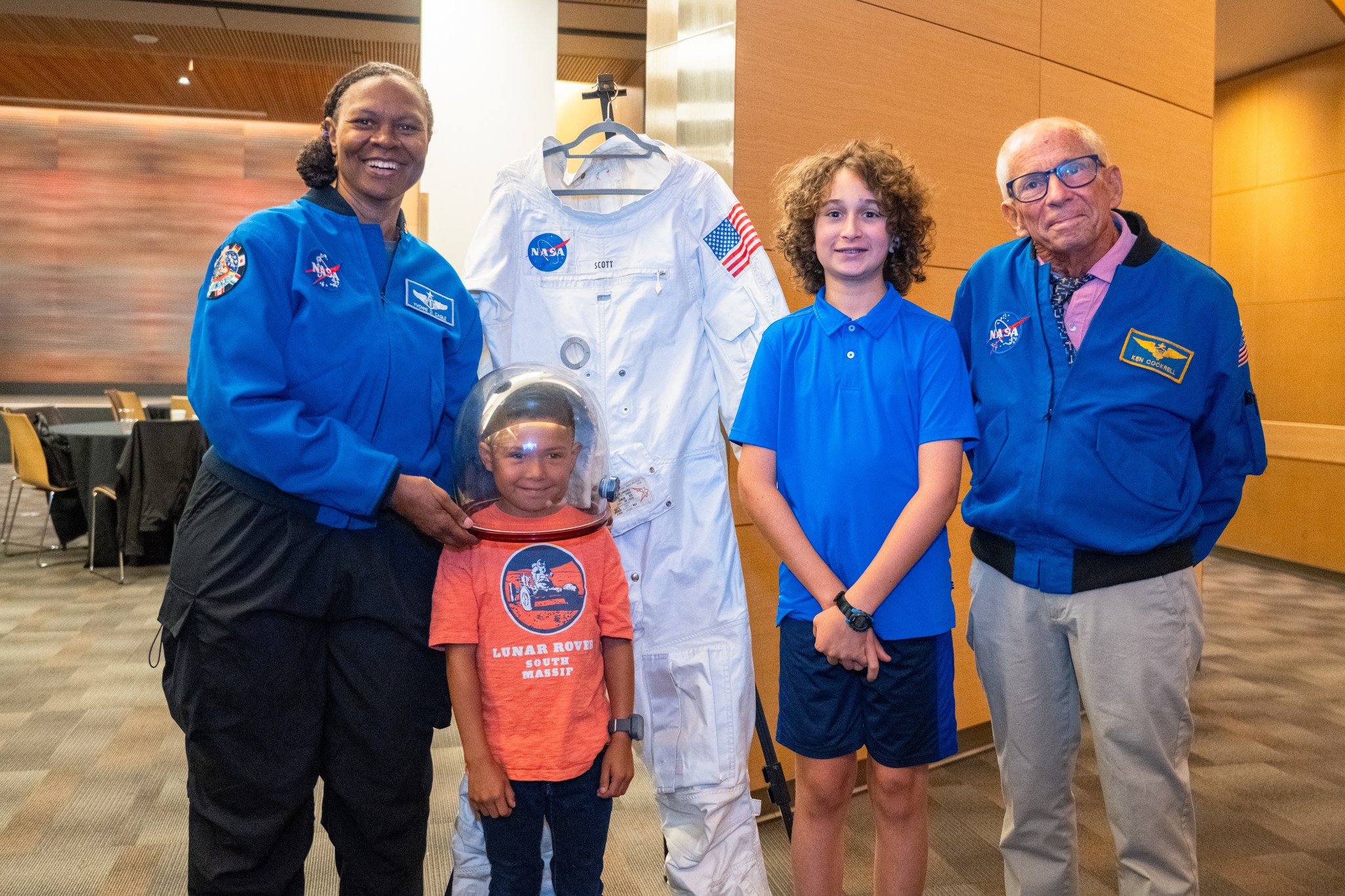

NASA astronauts, scientists, and researchers, and leadership from the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) met with cancer patients and gathered in a discussion about potential research opportunities and collaborations as part of President Biden and First Lady Jill Biden’s Cancer Moonshot initiative on Oct. 4. During the visit with patients, NASA astronaut Yvonne Cagle and former astronaut Kenneth Cockrell answered questions about spaceflight and life in space.
Ames and the University of California, Berkeley, expanded their partnership, organizing workshops to exchange on their areas of technical expertise, including in Advanced Air Mobility, and to develop ideas for the Berkeley Space Center, an innovation hub proposed for development at Ames’ NASA Research Park. Under a new agreement, NASA also will host supercomputing resources for UC Berkeley, supporting the development of novel computing algorithms and software for a wide variety of scientific and technology areas.